In the remainder of this chapter, we will discuss extensions to postings
list data structures and ways to increase the efficiency of using postings
lists.
Recall the basic postings list intersection operation from
Section 1.3 (page ![]() ): we walk through the two postings lists
simultaneously, in time linear in the total number of postings entries.
If the list lengths are
): we walk through the two postings lists
simultaneously, in time linear in the total number of postings entries.
If the list lengths are ![]() and
and ![]() , the intersection takes
, the intersection takes ![]() operations. Can we do better than this? That is, empirically, can we usually
process postings list intersection in sublinear time? We can, if the index isn't
changing too fast.
operations. Can we do better than this? That is, empirically, can we usually
process postings list intersection in sublinear time? We can, if the index isn't
changing too fast.
One way to do this is to use a skip list by augmenting postings lists with skip pointers (at indexing time), as shown in Figure 2.9 . Skip pointers are effectively shortcuts that allow us to avoid processing parts of the postings list that will not figure in the search results. The two questions are then where to place skip pointers and how to do efficient merging using skip pointers.
![\includegraphics[width=3.5in]{SkipLists.eps}](img106.png)
Postings lists with skip pointers.The postings intersection can use a skip pointer when the end point is still less than the item on the other list.
Consider first efficient merging, with Figure 2.9 as an
example. Suppose we've stepped through the lists in the figure until
we have matched ![]() on each list and moved it to the results
list. We advance both pointers, giving us
on each list and moved it to the results
list. We advance both pointers, giving us ![]() on the upper
list and
on the upper
list and ![]() on the lower list. The smallest item is then
the element
on the lower list. The smallest item is then
the element ![]() on the top list. Rather than simply
advancing the upper pointer, we first check the skip list pointer and
note that 28 is also less than 41. Hence we can follow the skip list
pointer, and then we advance the upper pointer to
on the top list. Rather than simply
advancing the upper pointer, we first check the skip list pointer and
note that 28 is also less than 41. Hence we can follow the skip list
pointer, and then we advance the upper pointer to ![]() .
We thus avoid stepping to
.
We thus avoid stepping to ![]() and
and ![]() on the upper list. A number of variant versions of postings list
intersection with skip pointers is possible depending on when exactly
you check the skip pointer. One version is shown in
Figure 2.10 . Skip pointers
will only be available for the original postings lists. For an
intermediate result in a complex query, the call
on the upper list. A number of variant versions of postings list
intersection with skip pointers is possible depending on when exactly
you check the skip pointer. One version is shown in
Figure 2.10 . Skip pointers
will only be available for the original postings lists. For an
intermediate result in a complex query, the call
![]() will always return false. Finally, note
that the presence of skip pointers only helps for AND queries,
not for OR queries.
will always return false. Finally, note
that the presence of skip pointers only helps for AND queries,
not for OR queries.
Where do we place skips? There is a tradeoff.
More skips means shorter skip spans, and that we are more likely to
skip. But it also means lots of comparisons to skip pointers, and lots
of space storing skip pointers.
Fewer skips means few pointer comparisons, but then long skip spans
which means that there will be fewer opportunities to skip.
A simple heuristic for placing skips, which has been found to work well
in practice, is that for a postings list of length ![]() , use
, use ![]() evenly-spaced skip pointers.
This heuristic can be improved upon; it ignores any details
of the
distribution of query terms.
evenly-spaced skip pointers.
This heuristic can be improved upon; it ignores any details
of the
distribution of query terms.
Building effective skip pointers is easy if an index is relatively static; it is harder if a postings list keeps changing because of updates. A malicious deletion strategy can render skip lists ineffective.
Choosing the optimal encoding for an inverted index is an ever-changing
game for the system builder, because it is strongly dependent on underlying computer
technologies and their relative speeds and sizes.
Traditionally, CPUs were slow, and so highly compressed techniques were
not optimal. Now CPUs are fast and disk is slow, so reducing disk
postings list size dominates. However, if you're running a search
engine with everything in memory then the equation changes again.
We discuss the impact of hardware parameters on index construction time
in Section 4.1 (page ![]() ) and the impact of index size on system speed
in Chapter 5 .
) and the impact of index size on system speed
in Chapter 5 .
Exercises.
[4,6,10,12,14,16,18,20,22,32,47,81,120,122,157,180]and for the other it is the one entry postings list:
[47].Work out how many comparisons would be done to intersect the two postings lists with the following two strategies. Briefly justify your answers:
xunit=0.6cm,arcangle=30and the following intermediate result postings list (which hence has no skip pointers):
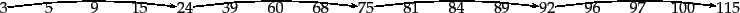
3 5 89 95 97 99 100 101Trace through the postings intersection algorithm in Figure 2.10 (page