



Next: The Bernoulli model
Up: Naive Bayes text classification
Previous: Naive Bayes text classification
Contents
Index
Relation to multinomial unigram language model
The multinomial NB model is formally identical to the
multinomial unigram language model
(Section 12.2.1 ,
page 12.2.1 ).
In particular, Equation 113 is a special case of
Equation 104 from page 12.2.1 ,
which we repeat here for 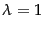 :
:
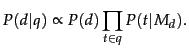 |
|
|
(120) |
The document 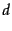 in text classification
(Equation 113) takes the role of the query in
language modeling (Equation 120) and the classes
in text classification
(Equation 113) takes the role of the query in
language modeling (Equation 120) and the classes
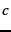 in text classification take the role of the documents
in text classification take the role of the documents
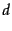 in language modeling. We used Equation 120
to rank documents according to the probability that they
are relevant to
the query
in language modeling. We used Equation 120
to rank documents according to the probability that they
are relevant to
the query 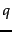 . In NB classification, we are
usually only interested in the top-ranked class.
. In NB classification, we are
usually only interested in the top-ranked class.
We also used MLE estimates in Section 12.2.2 (page ![[*]](http://nlp.stanford.edu/IR-book/html/icons/crossref.png) )
and encountered the problem of zero estimates owing to sparse
data (page 12.2.2 ); but instead of add-one
smoothing, we used a mixture of two distributions to address
the problem there.
Add-one smoothing is closely related to
add-
)
and encountered the problem of zero estimates owing to sparse
data (page 12.2.2 ); but instead of add-one
smoothing, we used a mixture of two distributions to address
the problem there.
Add-one smoothing is closely related to
add-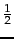 smoothing in
Section 11.3.4 (page
smoothing in
Section 11.3.4 (page ![[*]](http://nlp.stanford.edu/IR-book/html/icons/crossref.png) ).
).
Exercises.
- Why is
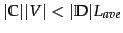 in
Table 13.2 expected to hold for most text
collections ?
in
Table 13.2 expected to hold for most text
collections ?




Next: The Bernoulli model
Up: Naive Bayes text classification
Previous: Naive Bayes text classification
Contents
Index
© 2008 Cambridge University Press
This is an automatically generated page. In case of formatting errors you may want to look at the PDF edition of the book.
2009-04-07
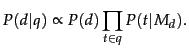
![]() )
and encountered the problem of zero estimates owing to sparse
data (page 12.2.2 ); but instead of add-one
smoothing, we used a mixture of two distributions to address
the problem there.
Add-one smoothing is closely related to
add-
)
and encountered the problem of zero estimates owing to sparse
data (page 12.2.2 ); but instead of add-one
smoothing, we used a mixture of two distributions to address
the problem there.
Add-one smoothing is closely related to
add-![]() smoothing in
Section 11.3.4 (page
smoothing in
Section 11.3.4 (page ![]() ).
).